OpenAI SSE (Server-Sent Events) Streaming API

Have you been working on an OpenAI project that uses the Chat GPT API? Do you want to stream the response to your application in real-time — as it's being generated?
In this article, I will walk you through the process of using OpenAI’s API to receive SSE to your server and forwarding those events to your client using SSE. The examples will be written in JavaScript, Python, and HTML.
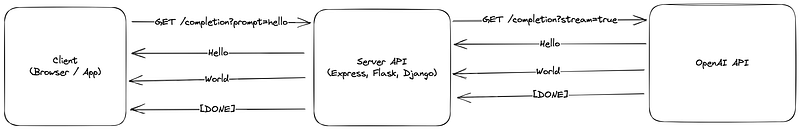
Workflow
-
The client creates an SSE
EventSourceto server endpoint with SSE configured. -
The server receives the request and sends a request to
OpenAI API using the
stream: trueparameter. - A server listens for server-side events from the OpenAI API connection created in step 2. For each event received, we can forward that message to our client. This creates a nested SSE event system where we proxy the OpenAI SSE back to our client, listening for the response. This also keeps our API secret because all the communication to OpenAI happens on our server.
-
After the client receives the entire response, OpenAI
will send a special message to let us know to close
the connection. The
[Done]message will signal that we can close the SSE connection to OpenAI, and our client can close the connection to our server.
Client Setup
First, we need to create a small client-side app to
receive the events from our web server. Create this file
in the web server directory so it can be served up later
by the same web server returning SSE events. The
EventSource
may need to be edited depending on the web server you
are using
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="result"></div>
<script>
var source = new EventSource("http://127.0.0.1:5000/completion");
source.onmessage = function(event) {
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML += event.data + "<br>";
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
Server Setup
The instructions below include multiple methods for setting up the server-side SSE web server. Choose one of the methods in your preferred programing language.
Flask
To set up Flask, you will need to set the OpenAI API key
in your environment or edit the code in
app.py
to add the key directly. Create the files below in the
same directory.
app.py
import os
import flask
import openai
from flask import Flask
openai.api_key = os.environ.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home():
return """
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>response:</h1>
<div id="result"></div>
<script>
var source = new EventSource("/completion");
source.onmessage = function(event) {
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML += event.data + "<br>";
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
"""
@app.route('/completion', methods=['GET'])
def completion_api():
def stream():
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="Hello world", stream=True)
for line in completion:
yield 'data: %s\n\n' % line.choices[0].text
return flask.Response(stream(), mimetype='text/event-stream')
@app.route('/completionChat', methods=['GET'])
def completion_api():
def stream():
completion = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model='gpt-3.5-turbo',
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello world"}],
stream=True)
for line in completion:
chunk = line['choices'][0].get('delta', {}).get('content', '')
if chunk:
yield 'data: %s\n\n' % chunk
return flask.Response(stream(), mimetype='text/event-stream')
requirements.txt
Flask>=1.0
openai
Run the Flask server from the directory where
app.py
was created, and visit the endpoint in your browser.
export FLASK_APP=app.py
export FLASK_ENV=development
flask run
Django
The file structure may look slightly different for your app, but the handler code can easily be copied.
urls.py
import os
import openai
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.http import StreamingHttpResponse, HttpResponse
openai.api_key = os.environ.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')
def stream(request):
def event_stream():
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="Hello world", stream=True)
for line in completion:
yield 'data: %s\n\n' % line.choices[0].text
return StreamingHttpResponse(event_stream(), content_type='text/event-stream')
def streamChat(request):
def event_stream():
completion = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model='gpt-3.5-turbo',
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello world"}],
stream=True)
for line in completion:
chunk = line['choices'][0].get('delta', {}).get('content', '')
if chunk:
yield 'data: %s\n\n' % chunk
return StreamingHttpResponse(event_stream(), content_type='text/event-stream')
def home(request):
return HttpResponse("""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>response:</h1>
<div id="result"></div>
<script>
var source = new EventSource("/completion");
source.onmessage = function(event) {
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML += event.data + "<br>";
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
""")
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('completion', stream),
path('completionChat', streamChat),
path('', home)
]
Run the Django app and open a browser to the root endpoint.
python manage.py runserver
Node Express
Set up a simple server to request OpenAI API and forward
the SSE requests to the web server client. The end
message
[DONE]
can also be forwarded to your client to end the request
session.
server.js
const express = require('express')
const { Configuration, OpenAIApi } = require("openai");
const configuration = new Configuration({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
});
const openai = new OpenAIApi(configuration);
const app = express()
const port = 3000
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(`
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>response:</h1>
<div id="result"></div>
<script>
var source = new EventSource("/completion");
source.onmessage = function(event) {
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML += event.data + "<br>";
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
`)
})
app.get('/completion', (req, res) => {
res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'no-cache');
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/event-stream');
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
res.setHeader('Connection', 'keep-alive');
res.flushHeaders(); // flush the headers to establish SSE with client
const response = openai.createCompletion({
model: "text-davinci-003",
prompt: "hello world",
max_tokens: 100,
temperature: 0,
stream: true,
}, { responseType: 'stream' });
response.then(resp => {
resp.data.on('data', data => {
const lines = data.toString().split('\n').filter(line => line.trim() !== '');
for (const line of lines) {
const message = line.replace(/^data: /, '');
if (message === '[DONE]') {
res.end();
return
}
const parsed = JSON.parse(message);
res.write(`data: ${parsed.choices[0].text}\n\n`)
}
});
})
})
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`)
})
Run the server and open a browser to see the output.
node server.js
End SSE session
When the entire OpenAI response has been returned, you
can terminate the
EventSource
on the client side. OpenAI will always send a
[DONE]
message to inform you when the answer is completed.
var source = new EventSource("/completion");
source.onmessage = function(event) {
if (event.data === '[DONE]') {
source.close()
} else {
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML += event.data + "<br>";
}
};
SSE Over POST Request
Sometimes its easier to work with a POST request instead
of
EventSource
required GET request, because of the data needed to make
our request to OpenAI. Here is another post I made about
this subject
https://medium.com/@david.richards.tech/sse-server-sent-events-using-a-post-request-without-eventsource-1c0bd6f14425. Below I included two small snippets with javascript
and python flask code to complete this.
const response = await fetch('/completions/chat', {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
prompt: prompt,
}),
});
if (!response.body) return;
const reader = response.body
.pipeThrough(new TextDecoderStream())
.getReader();
while (true) {
var { value, done } = await reader.read();
if (done) break;
document.getElementById("result").innerHTML += event.data
}
@app.route('/completions/chat', methods=['POST'])
def completion_api():
def stream():
completion = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model='gpt-3.5-turbo',
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": request.get_json().get('prompt')}],
stream=True)
for line in completion:
chunk = line['choices'][0].get('delta', {}).get('content', '')
if chunk:
yield chunk
return flask.Response(stream(), mimetype='text/event-stream')
Thank you for reading! Stay tuned for more.